Many data center
operators face a crossroads now as they consider the strategic
implications of new demands on their IT infrastructure and the new choices
that they have when it comes to a cloud continuum of deployment options.
These hybrid choices span not only cloud hosts and providers, but
also platform technologies such as containers, intelligent network fabrics,
serverless computing, and, yes, even good old bare metal.
For thousands of companies, the evaluation of their cloud choices also impacts how they on can help conquer the “VMware tax” by moving beyond a traditional server virtualization legacy.
For thousands of companies, the evaluation of their cloud choices also impacts how they on can help conquer the “VMware tax” by moving beyond a traditional server virtualization legacy.
The complexity of
choice goes further because long-term decisions about technology must also
include implications for long-term recurring costs -- as well as business continuity. As IT architects and operators seek to best map a future
from a VMware hypervisor
and traditional data center architecture, they also need to
consider openness and lock-in.
Our panelists review how public cloud providers and managed service providers (MSPs) are sweetening the deal to transition to predicable hybrid cloud models. The discussion is designed to help IT leaders to find the right trade-offs and the best rationale for making the strategic decisions for their organization's digital transformation.
The panel consists of David Grimes, Vice President of Engineering at Navisite; David Linthicum, Chief Cloud Strategy Officer at Deloitte Consulting, and Tim Crawford, CIO Strategic Advisor at AVOA. The discussion is moderated by BriefingsDirect's Dana Gardner, principal analyst at Interarbor Solutions.
Here are some excerpts:
Gardner: Clearly, over the past decade or two, countless virtual machines have been spun up to redefine data center operations and economics. And as server and storage virtualization were growing dominant, VMware was crowned -- and continues to remain -- a virtualization market leader. The virtualization path broadened over time from hypervisor adoption to platform management, network virtualization, and private cloud models. There have been a great many good reasons for people to exploit virtualization and adopt more of a software-defined data center (SDDC) architecture. And that brings us to where we are today.
Dominance in virtualization, however, has not translated into an automatic path from virtualization to a public-private cloud continuum. Now, we are at a crossroads, specifically for the economics of hybrid cloud models. Pay-as-you-go consumption models have forced a reckoning on examining your virtual machine past, present, and future.
Linthicum: I've been with Deloitte Consulting for six months. I'm
the Chief Cloud Strategy Officer, the thought leadership guy, trying to
figure out where the cloud computing ball is going to be kicked and what
the clients are doing, what's going to be important in the years to come.
Prior to that I was with Cloud Technology Partners. We sold that to Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) last year. I’ve written 13 books. And I do the cloud blog on
InfoWorld, and also do a lot of radio and TV. And the podcast, Dana.
Gardner: Yes, of course. You've been doing that podcast for quite a while. Tim Crawford, tell us about yourself and AVOA.
Crawford: After spending 20-odd years within the rank and file of the IT organization, also as a CIO, I bring a unique perspective to the conversation, especially about transformational organizations. I work with Fortune 250 companies, many of the Fortune 50 companies, in terms of their transformation, mostly business transformation. I help them explore how technology fits into that, but I also help them along their journey in understanding the difference between the traditional and transformational. Like Dave, I do a lot of speaking, a fair amount of writing and, of course, with that comes with travel and meeting a lot of great folks through my journeys.
And then you have the third piece to that trifecta, which are the overall
business demands. We saw a very significant change in customer buying
behavior at the same time, which is people were looking for things now.
We saw the uptick of Amazon use and away
from traditional retail, and that trend really kicked into gear around
the same time. All of these together lead into this shift to demand
for a different kind of model, looking at OpEx versus CapEx.
Gardner: Dave, you and I have talked about this a lot over the past 10 years, economics being a driver. But you don't necessarily always save money by going to cloud. To me, what I see in these results is not just seeking lower total cost -- but simplification, consolidation and rationalization for what enterprises do spend on IT. Does that make sense and is that reflected in your practice?
One of the things
in the survey results that does surprise me is the relatively low scoring
for the operations complexity and support difficulties. With the pace of
technology innovation happening, and even within VMware, within the
enterprise context, but certainly within the context of the cloud
platforms, Azure in particular, the skillsets to use those platforms,
manage them effectively and take the biggest advantage of them are in
exceedingly high demand. Many organizations are struggling to acquire
and retain that talent. That's certainly been my experience in with
dealing with my clients and prospects.
Gardner: Now that we know why people want to move, let's look at what it is that's preventing them from moving. What are the chief obstacles that are preventing those in our audience from moving off of a legacy environment like VMware?
The third concern,
a close tie, are issues around compliance, security, and regulatory
restrictions from moving to the cloud. Complexity and uncertainty that the
migration process will be successful, are also of concern.
They're worried about that lift and shift process.
Grimes: There are certainly those hyperscale players, but there are
also a number of regional public cloud players in the form of the VMware partner ecosystem.
And I think when we talk about public versus private, we also need to make
a distinction between public hyperscale and public cloud that still could be
VMware-based.
I think one interesting thing that ties back to my earlier comments is when you look at Microsoft Azure and their Azure Stack hybrid cloud strategy. If you flip that 180 degrees, and consider the VMware on AWS strategy, I think we'll continue to see that type of thing play out going forward. Both of those approaches actually reflect the need to be able to deliver the legacy enterprise workload in a way that is adjacent from an equivalence of technology as well as a latency perspective. Because one thing that's often overlooked is the need to examine the hybrid cloud deployment models via the acceptable latency between applications that are inherently integrated. That can often be a deal-breaker for a successful implementation.
What we'll see is this continued evolution of ensuring that we can solve what I see as a decade-forward problem. And that is, as organizations continue to reinvent their applications portfolio they must also evolve the way that they actually build and deliver applications while continuing to be able to operate their business based on the legacy stack that's driving day-to-day operations.
Linthicum: I thought there would be a few that would pick VMware on AWS, but it looks like the audience doesn't necessarily see that that's going to be the solution. Everything else is not surprising. It's aligned with what we see in the marketplace right now. Public cloud movement to Azure, Google Cloud and then also the movement to complex clouds like hybrid and multi-cloud also seem to be the two trends worth seeing right now in the space, and this is reflective of that.
Gardner: Let's move our discussion on. It's time to define the right trade-offs and rationale when we think about these taxing choices. We know that people want to improve, they don't want to be locked in, they want good economics, and they're probably looking for a long-term solution.
And so I think one of the key things that folks should do is
consider carefully how they partner regardless of where they are in that
journey, if they are on step one or step three, to continue that journey
is going to be critical on selecting the right partner to help them.
Gardner: Dave, when you're looking at risk versus reward, cost versus benefits, when you're wanting to hedge bets, what is it about Microsoft Azure and Azure Stack in particular that help solve that? It seems to me that they've gone to great pains to anticipate the state of the market right now and to try to differentiate themselves. Is there something about the Microsoft approach that is, in fact, differentiated among the hyperscalers?
Grimes: Ceridian is a global human capital management
company, global being a key point. They are growing like gangbusters and
have been with Navisite for quite some time. It's been a very long
journey.
Linthicum: Ultimately, the compute aspect of an application and the
data aspect of that application really should be decoupled. Then, if you
want to, you can assemble them on different platforms. I would typically
think that we're going to place them either on all public or all private,
but you can certainly do one on private and one on public, and one on
public and one on private, and link them that way.
Listen to the podcast. Find it on iTunes. Read a full transcript or download a copy.
Our panelists review how public cloud providers and managed service providers (MSPs) are sweetening the deal to transition to predicable hybrid cloud models. The discussion is designed to help IT leaders to find the right trade-offs and the best rationale for making the strategic decisions for their organization's digital transformation.
The panel consists of David Grimes, Vice President of Engineering at Navisite; David Linthicum, Chief Cloud Strategy Officer at Deloitte Consulting, and Tim Crawford, CIO Strategic Advisor at AVOA. The discussion is moderated by BriefingsDirect's Dana Gardner, principal analyst at Interarbor Solutions.
Here are some excerpts:
Gardner: Clearly, over the past decade or two, countless virtual machines have been spun up to redefine data center operations and economics. And as server and storage virtualization were growing dominant, VMware was crowned -- and continues to remain -- a virtualization market leader. The virtualization path broadened over time from hypervisor adoption to platform management, network virtualization, and private cloud models. There have been a great many good reasons for people to exploit virtualization and adopt more of a software-defined data center (SDDC) architecture. And that brings us to where we are today.
Dominance in virtualization, however, has not translated into an automatic path from virtualization to a public-private cloud continuum. Now, we are at a crossroads, specifically for the economics of hybrid cloud models. Pay-as-you-go consumption models have forced a reckoning on examining your virtual machine past, present, and future.
My first question to the panel is ... What are you now seeing
as the top drivers for people to reevaluate their enterprise IT
architecture path?
The cloud-migration challenge
Grimes: It's a really good question. As you articulated it, VMware
radically transformed the way we think about deploying and managing IT infrastructure,
but cloud has again redefined all of that. And the things you point out
are exactly what many businesses face today, which is supporting a set of
existing applications that run the business. In most cases they run on very
traditional infrastructure models, but they're looking at what cloud now offers
them in terms of being able to reinvent that application portfolio.
 |
| Grimes |
But that's going to be a multiyear journey in most cases. One of
the things that I think about as the next wave of transformation takes
place is how do we enable development in these new models, such as
containers and serverless, and using all of the platform services of the
hyperscale cloud. How do we bring those to the enterprise in a way that
will keep them adjacent to the workloads? Separating off in the
application and the data is very challenging.
Gardner: Dave, organizations would probably have it easier if they're just going to go from running their on-premises apps to a single public cloud provider. But more and more, we're quite aware that that's not an easy or even a possible shift. So, when organizations are thinking about the hybrid cloud model, and moving from traditional virtualization, what are some of the drivers to consider for making the right hybrid cloud model decision, where they can do both on-premises private cloud as well as public cloud?
Gardner: Dave, organizations would probably have it easier if they're just going to go from running their on-premises apps to a single public cloud provider. But more and more, we're quite aware that that's not an easy or even a possible shift. So, when organizations are thinking about the hybrid cloud model, and moving from traditional virtualization, what are some of the drivers to consider for making the right hybrid cloud model decision, where they can do both on-premises private cloud as well as public cloud?
Know what you have, know what you need
Linthicum: It really comes down to the profiles of the workloads, the
databases, and the data that you're trying to move. And one of the
things that I tell clients is that cloud is not necessarily something
that's automatic. Typically, they are going to be doing something that may
be even more complex than they have currently. But let's look at
the profiles of the existing workloads and the data -- including security,
governance needs, what you're running, what platforms you need to move to --
and that really kind of dictates which resources we want to put them on.
As an architect, when I look at the resources out there, I see traditional
systems, I see private clouds, virtualization -- such as VMware -- and then
the public cloud providers. And many times, the choice is going to be all four.
And having pragmatic hybrid clouds, which are paired with
traditional systems and private and public clouds -- means multiple clouds
at the same time. And so, this really becomes an analysis in terms of how
you're going to look at the existing as-is state. And the to-be state is
really just a functional matter of what the to-be state should be based on
the business requirements that you see. So, it's a little easier than
I think most people think, but I think the outcome is typically going to
be more expensive and more complex than they originally anticipated.
Gardner: Tim Crawford, do people under-appreciate the complexity of moving from a highly virtualized on-premises, traditional data center to hybrid cloud?
Crawford: Yes, absolutely. Dave's right. There are a lot of assumptions that we take as IT professionals and we bring them to cloud, and then find that those assumptions kind of fall flat on their face. Many of the myths and misnomers of cloud start to rear their ugly heads. And that's not to say that cloud is bad; cloud is great. But we have to be able to use it in a meaningful way, and that's a very different way than how we've operated our corporate data centers for the last 20, 30, or 40 years. It's almost better if we forget what we've learned over the last 20-plus years and just start anew, so we don't bring forward some of those assumptions.
And I want to touch on something else that I think is really important
here, which has nothing to do with technology but has to do
with organization and culture, and some of the other drivers that go into
why enterprises are leveraging cloud today. And that is that the world is
changing around us. Our customers are changing, the speed in which we have
to respond to demand and need is changing, and our traditional corporate
data center stacks just aren't designed to be able to make those kinds of
shifts.
 |
| Linthicum |
Gardner: Tim Crawford, do people under-appreciate the complexity of moving from a highly virtualized on-premises, traditional data center to hybrid cloud?
Crawford: Yes, absolutely. Dave's right. There are a lot of assumptions that we take as IT professionals and we bring them to cloud, and then find that those assumptions kind of fall flat on their face. Many of the myths and misnomers of cloud start to rear their ugly heads. And that's not to say that cloud is bad; cloud is great. But we have to be able to use it in a meaningful way, and that's a very different way than how we've operated our corporate data centers for the last 20, 30, or 40 years. It's almost better if we forget what we've learned over the last 20-plus years and just start anew, so we don't bring forward some of those assumptions.
 |
| Crawford |
And so that's why it’s going to be a mix of cloud and corporate
data centers. We're going to be spread
across these different modes like peanut butter in a way. But having the
flexibility, as Dave said, to leverage the right solution for the right
application is really, really important. Cloud presents a new model because our
needs have not been able to be fulfilled in the past.
Gardner: David Grimes, application developers helped drive initial cloud adoption. These were new apps and workloads of, by, and for the cloud. But when we go to enterprises that have a large on-premises virtualization legacy -- and are paying high costs as a result -- how frequently are we seeing people move existing workloads into a cloud, private or public? Is that gaining traction now?
Gardner: David Grimes, application developers helped drive initial cloud adoption. These were new apps and workloads of, by, and for the cloud. But when we go to enterprises that have a large on-premises virtualization legacy -- and are paying high costs as a result -- how frequently are we seeing people move existing workloads into a cloud, private or public? Is that gaining traction now?
Lift and shift the workload
Grimes: It absolutely is. That's really been a core part of our business
for a while now, certainly the ability to lift and shift out of the
enterprise data center. As Dave said, the workload is the critical factor.
You always need to understand the workload to know which platform to put
it on. That's a given. With a lot of that existing legacy
application stacks running in traditional infrastructure models, very
often those get lifted and shifted into a like-model -- but in a
hosting provider's data center. That’s because many CIOs have a mandate to
close down enterprise data centers and move to the cloud. But that does,
of course, mean a lot of different things.
You mentioned the push by developers to get into the cloud, and really that was what I was alluding to in my earlier comments. Such a reinventing of the enterprise application portfolio has often been led by the development that takes place within the organization. Then, of course, there are all of the new capabilities offered by the hyperscale clouds -- all of them, but notably some of the higher-level services offered by Azure, for example. You're going to end up in a scenario where you've got workloads that best fit in the cloud because they're based on the services that are now natively embodied and delivered as-a-service by those cloud platforms.
You mentioned the push by developers to get into the cloud, and really that was what I was alluding to in my earlier comments. Such a reinventing of the enterprise application portfolio has often been led by the development that takes place within the organization. Then, of course, there are all of the new capabilities offered by the hyperscale clouds -- all of them, but notably some of the higher-level services offered by Azure, for example. You're going to end up in a scenario where you've got workloads that best fit in the cloud because they're based on the services that are now natively embodied and delivered as-a-service by those cloud platforms.
But you're going to still have that legacy stack that still
needs to leave the enterprise data center. So, the hybrid models are prevailing,
and I believe will continue to prevail. And that's reflected in Microsoft's
move with Azure Stack, of making much of the Azure platform available to hosting
providers to deliver private Azure in a way that can engage and interact
with the hyperscale Azure cloud. And with that, you can position
the right workloads in the right environment.
Gardner: Now that we're into the era of lift and shift, let's look at some of the top reasons why. We will ask our audience what their top reasons are for moving off of legacy environments like VMware. But first let’s learn more about our panelists. David Grimes, tell us about your role at Navisite and more about Navisite itself.
Gardner: Now that we're into the era of lift and shift, let's look at some of the top reasons why. We will ask our audience what their top reasons are for moving off of legacy environments like VMware. But first let’s learn more about our panelists. David Grimes, tell us about your role at Navisite and more about Navisite itself.
Panelist profiles
Grimes: I've been with Navisite for 23
years, really most of my career. As VP of Engineering, I run our product
engineering function. I do a lot of the evangelism for the organization.
Navisite's a part of Spectrum Enterprise, which is the enterprise division of Charter. We deliver voice, video, and data services to the
enterprise client base of Navisite, and also deliver cloud services to
that same base. It's been a very interesting 20-plus years to see the
continued evolution of managed infrastructure delivery models rapidly
accelerating to where we are today.
Gardner: Dave Linthicum, tell us a bit about yourself, particularly what you're doing now at Deloitte Consulting.
Gardner: Dave Linthicum, tell us a bit about yourself, particularly what you're doing now at Deloitte Consulting.
It's been a very interesting 20-plus years to see the continued evolution of managed infrastructure delivery models.
Gardner: Yes, of course. You've been doing that podcast for quite a while. Tim Crawford, tell us about yourself and AVOA.
Crawford: After spending 20-odd years within the rank and file of the IT organization, also as a CIO, I bring a unique perspective to the conversation, especially about transformational organizations. I work with Fortune 250 companies, many of the Fortune 50 companies, in terms of their transformation, mostly business transformation. I help them explore how technology fits into that, but I also help them along their journey in understanding the difference between the traditional and transformational. Like Dave, I do a lot of speaking, a fair amount of writing and, of course, with that comes with travel and meeting a lot of great folks through my journeys.
Survey says: It’s economics
Gardner: Let's now look at our first audience survey results. I'd
like to add that this is not scientific. This is really an anecdotal look
at where our particular audience is in terms of their journey. What are
their top reasons for moving off of legacy environments like VMware?
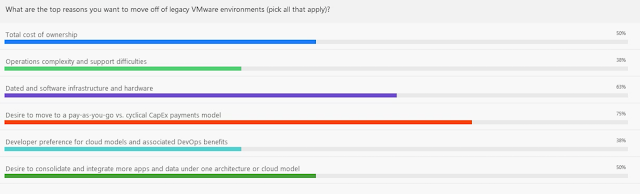
The top reason, at
75 percent, is a desire to move to a pay-as-you-go versus a cyclical CapEx
model. So, the economics here are driving the move from traditional
to cloud. They're also looking to get off of dated software and hardware
infrastructure. A lot of people are running old hardware, it's not that
efficient, can be costly to maintain and in some cases, difficult or
impossible, to replace. There is a tie at 50 percent each in concern about
the total cost of ownership, probably trying to get that down, and a
desire to consolidate and integrate more apps and data, so seeking a
transformation of their apps and data.
Coming up on the lower end of their motivations are complexity and support difficulties, and the developer preference for cloud models. So, the economics are driving this shift. That should come as no surprise, Tim, that a lot of people are under pressure to do more with less and to modernize at the same time. The proverbial changing of the wings of the airplane while keeping it flying. Is there any more you would offer in terms of the economic drivers for why people should consider going from a traditional data center to a hybrid IT environment?
Crawford: It's not surprising, and the reason I say that is this economic upheaval actually started about 10 years ago when we really felt that economic downturn. It caused a number of organizations to say, "Look, we don't have the money to be able to upgrade or replace equipment on our regular cycles."
Coming up on the lower end of their motivations are complexity and support difficulties, and the developer preference for cloud models. So, the economics are driving this shift. That should come as no surprise, Tim, that a lot of people are under pressure to do more with less and to modernize at the same time. The proverbial changing of the wings of the airplane while keeping it flying. Is there any more you would offer in terms of the economic drivers for why people should consider going from a traditional data center to a hybrid IT environment?
Crawford: It's not surprising, and the reason I say that is this economic upheaval actually started about 10 years ago when we really felt that economic downturn. It caused a number of organizations to say, "Look, we don't have the money to be able to upgrade or replace equipment on our regular cycles."
And
so instead of having a four-year cycle for servers, or a five-year
cycle for storage, or in some cases as much as 10-plus cycle for
network -- they started kicking that can down the road. When the economic
situation improved, rather than put money back into infrastructure, people
started to ask, "Are there other approaches that we can take?"
Now, at the same time, cloud was really beginning to mature and become a viable
solution, especially for mid- to large- enterprises. And so, the combination
of those two opened the door to a different possibility that didn't have
to do with replacing the hardware in corporate data centers.
Instead of having a four-year cycle for servers or five-year cycle for storage, they started kicking the can down the road.
Gardner: Dave, you and I have talked about this a lot over the past 10 years, economics being a driver. But you don't necessarily always save money by going to cloud. To me, what I see in these results is not just seeking lower total cost -- but simplification, consolidation and rationalization for what enterprises do spend on IT. Does that make sense and is that reflected in your practice?
Savings, strategy and speed
Linthicum: Yes, it is, and I think that the primary reason for moving to
the cloud has morphed in the last five years from the CapEx saving money, operational
savings model into the need for strategic value. That means gaining agility,
ability to scale your systems up as you need to, to adjust to the needs of
the business in the quickest way -- and be able to keep up with the speed
of change.
A lot of the Global
2,000 companies out there are
having trouble maintaining change within the organization, to keep up with
change in their markets. I think that's really going to be the death of a
thousand cuts if they don't fix it. They're seeing cloud as an enabling
technology to do that.
In other words, with
cloud they can have the resources they need, they can get to the
storage levels they need, they can manage the data that they need -- and
do so at a price point that typically is going to be lower than the
on-premise systems. That's why they're moving in that direction. But like
we said earlier, in doing so they're moving into more complex models.
They're typically going to be spending a bit more money, but the value of
IT -- in its ability to delight the business in terms of new capabilities --
is going to be there. I think that's the core metric we need to consider.
Gardner: David, at Navisite, when it comes to cost balanced by the business value from IT, how does that play out in a managed hosting environment? Do you see organizations typically wanting to stick to what they do best, which is create apps, run business processes, and do data science, rather than run IT systems in and out of every refresh cycle? How is this shaking out in the managed services business?
Grimes: That's exactly what I'm seeing. Companies are really moving toward focusing on their differentiation. Running infrastructure has become almost like having power delivered to your data center. You need it, it's part of the business, but it's rarely differentiating. So that's what we're seeing.
Gardner: David, at Navisite, when it comes to cost balanced by the business value from IT, how does that play out in a managed hosting environment? Do you see organizations typically wanting to stick to what they do best, which is create apps, run business processes, and do data science, rather than run IT systems in and out of every refresh cycle? How is this shaking out in the managed services business?
Grimes: That's exactly what I'm seeing. Companies are really moving toward focusing on their differentiation. Running infrastructure has become almost like having power delivered to your data center. You need it, it's part of the business, but it's rarely differentiating. So that's what we're seeing.
Running
infrastructure has become almost like having power delivered to your
data center. You need it, but its rarely differentiating.
Gardner: Now that we know why people want to move, let's look at what it is that's preventing them from moving. What are the chief obstacles that are preventing those in our audience from moving off of a legacy environment like VMware?
There's more than just a technological decision here. Dell Technologies is the major controller of VMware, even with VMware being a
publicly traded company. But Dell Technologies, in order to go private,
had to incur enormous debt, still in the vicinity of $48 billion. There's
been reports recently of a reverse merger, where VMware as a public
company will take over Dell as a private company. The markets didn't necessarily go for that, and it creates a bit of confusion and concern in the
market. So Dave, is this something IT operators and architects should concern
themselves with when they're thinking about which direction to go?
Linthicum: Ultimately, we need to look at the health of the company
we're buying hardware and software from in terms of their ability to be
around over the next few years. The reality is that VMware, Dell, and
[earlier Dell merger target] EMC are mega forces in terms of a legacy footprint in a majority
of data centers. I really don't see any need to be concerned about the
viability of that technology. And when I look at viability of companies, I
look at the viability of the technology, which can be bought and sold, and
the intellectual property can be traded off to other companies. I don't
think the technology is going to go away, it's just too much of a
cash cow. And the reality is, whoever owns VMware is going to be able to
make a lot of money for a long period of time.
Gardner: Tim, should organizations be concerned in that they want to have independence as VMware customers and not get locked in to a hardware vendor or a storage vendor at the same time? Is there concern about VMware becoming too tightly controlled by Dell at some point?
Gardner: Tim, should organizations be concerned in that they want to have independence as VMware customers and not get locked in to a hardware vendor or a storage vendor at the same time? Is there concern about VMware becoming too tightly controlled by Dell at some point?
Partnership prowess
Crawford: You always have to think about who it is that you're
partnering with. These days when you make a purchase as an
IT organization, you're really buying into a partnership, so you're buying
into the vision and direction of that given company.
And I agree with
Dave about Dell, EMC, and VMware in that they're going to be around for a
long period of time. I don't think that's really the factor to be
as concerned with. I think you have to look beyond that.
You have to look at
what it is that your business needs, and how does that start to influence
changes that you make organizationally in terms of where you focus your
management and your staff. That means moving up the chain, if you
will, and away from the underlying infrastructure and into applications
and things closely tied to business advantage.
As you start to do
that, you start to look at other opportunities beyond just virtualization.
You start breaking down the silos, you start breaking down the components
into smaller and smaller components -- and you look at the different
modes of system delivery. That's really where cloud starts to play a role.
Gardner: Let's look now to our audience for what they see as important. What are the chief obstacles preventing you from moving off of a legacy virtualization environment? Again, the economics are quite prevalent in their responses.
Gardner: Let's look now to our audience for what they see as important. What are the chief obstacles preventing you from moving off of a legacy virtualization environment? Again, the economics are quite prevalent in their responses.
By a majority,
they are not sure that there's sufficient return on investment (ROI) benefits.
They might be wondering why they should move at all. Their fear of a
lock-in to a primary cloud model is also a concern. So, the economics
and lock-in risk are high, not just from being stuck on a virtualization
legacy -- but also concern about moving forward. Maybe they're like the
deer in the headlights.
You
have to look at what it is that your business needs, and how does that
start to influence changes that you make organizationally, of where you
focus your management and your staff.
They are less
concerned about lack of support for moving from the C-Suite or business
leadership, of not getting buy-in from the top. So … If it's working,
don't fix it, I suppose, or at least don't break it. And the last issue of
concern, very low, is that it’s still too soon to know which cloud choices
are best.
So, it's not that they don't understand what's going on with
cloud, they're concerned about risk, and complexity of staying is a
concern -- but complexity of moving is nearly as big of a concern. David,
anything in these results that jump out to you?
Feel the fear and migrate anyway
Grimes: Of those not being sure of the ROI benefits, that's been a
common thread for quite some time in terms of looking at these cloud migrations.
But in our experience, what I've seen are clients choosing to move to a VMware cloud hosted by Navisite. They ultimately end up unlocking
the business agility of their cloud, even if they weren't 100 percent sure
going into it that they would be able to.
But time and time
again, moving away from the enterprise data center, repurposing the spend
on IT resources to become more valuable to the business -- as opposed to
the traditional keeping the lights on function -- has played out on a
fairly regular basis.
I agree with the audience and the response here around the fear of lock-in. And it's not just lock-in from a basic deployment infrastructure perspective, it's fear of lock-in if you choose to take advantage of a cloud’s higher-level services, such as data analytics or all the different business things that are now as-a-service. If you buy into them, you certainly increase your ability to deliver. Your own pace of innovation can go through the roof -- but you're often then somewhat locked in.
I agree with the audience and the response here around the fear of lock-in. And it's not just lock-in from a basic deployment infrastructure perspective, it's fear of lock-in if you choose to take advantage of a cloud’s higher-level services, such as data analytics or all the different business things that are now as-a-service. If you buy into them, you certainly increase your ability to deliver. Your own pace of innovation can go through the roof -- but you're often then somewhat locked in.
You're buying into a particular service model, a set of APIs,
et cetera. It's a form of lock-in. It is avoidable if you want to
build in layers of abstraction, but it's not necessarily the end of the
world either. As with everything, there are trade-offs. You're getting a lot of
business value in your own ability to innovate and deliver quickly, yes, but
it comes at the cost of some lock-in to a particular platform.
Gardner: Dave, what I'm seeing here is people explaining why hybrid is important to them, that they want to hedge their bets. All or nothing is too risky. Does that make sense to you, that what these results are telling us is that hybrid is the best model because you can spread that risk around?
Gardner: Dave, what I'm seeing here is people explaining why hybrid is important to them, that they want to hedge their bets. All or nothing is too risky. Does that make sense to you, that what these results are telling us is that hybrid is the best model because you can spread that risk around?
IT in the balance between past and future
Linthicum: Yes, I think it does say that. I live this on a daily
basis in terms of ROI benefits and concern about not having enough, and
also the lock-in model. And the reality is that when you get to an
as-is architecture state, it's going to be a variety -- as we mentioned
earlier – of resources that we're going to leverage.
So, this is not
all about taking traditional systems – and the application workloads
around traditional systems -- and then moving them into the cloud and
shutting down the traditional systems. That won't work. This is about a
balance or modernization of technology. And if you look at that, all bets
are on the table -- including traditional, including private cloud,
and public cloud, and hybrid-based computing. Typically, it's going to be
the best path to success at looking at all of that. But like I said, the
solution's really going to be dependent on the requirements on the
business and what we're looking at.
Going forward, these kinds of decisions are falling into a pattern, and I think that we're seeing that this is not necessarily going to be pure-cloud play. This is not necessarily going to be pure traditional play, or pure private cloud play. This is going to be a complex architecture that deals with a private and public cloud paired with traditional systems.
Going forward, these kinds of decisions are falling into a pattern, and I think that we're seeing that this is not necessarily going to be pure-cloud play. This is not necessarily going to be pure traditional play, or pure private cloud play. This is going to be a complex architecture that deals with a private and public cloud paired with traditional systems.
And so, people who do want to hedge their bets will do that
around making the right decisions that they leverage the right resources
for the appropriate task at hand. I think that's going to be the winning
end-point. It's not necessarily moving to the platforms that we think are cool,
or that we think can make us more money -- it's about localization of the
workloads on the right platforms, to gain the right fit.
Gardner: From the last two survey result sets, it appears incumbent on legacy providers like VMware to try to get people to stay on their designated platform path. But at the same time, because of this inertia to shift, because of these many concerns, the hyperscalers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services also need to sweeten their deals. What are these other cloud providers doing, David, when it comes to trying to assuage the enterprise concerns of moving wholesale to the cloud?
Gardner: From the last two survey result sets, it appears incumbent on legacy providers like VMware to try to get people to stay on their designated platform path. But at the same time, because of this inertia to shift, because of these many concerns, the hyperscalers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services also need to sweeten their deals. What are these other cloud providers doing, David, when it comes to trying to assuage the enterprise concerns of moving wholesale to the cloud?
It's
not moving to the platforms that we think are cool, or that can make us
money, it's about localization of the workloads on the right platforms,
to get the right fit.
I think one interesting thing that ties back to my earlier comments is when you look at Microsoft Azure and their Azure Stack hybrid cloud strategy. If you flip that 180 degrees, and consider the VMware on AWS strategy, I think we'll continue to see that type of thing play out going forward. Both of those approaches actually reflect the need to be able to deliver the legacy enterprise workload in a way that is adjacent from an equivalence of technology as well as a latency perspective. Because one thing that's often overlooked is the need to examine the hybrid cloud deployment models via the acceptable latency between applications that are inherently integrated. That can often be a deal-breaker for a successful implementation.
What we'll see is this continued evolution of ensuring that we can solve what I see as a decade-forward problem. And that is, as organizations continue to reinvent their applications portfolio they must also evolve the way that they actually build and deliver applications while continuing to be able to operate their business based on the legacy stack that's driving day-to-day operations.
Moving solutions
Gardner: Our final survey question asks What are your current plans
for moving apps and data from a legacy environment like VMware, from a
traditional data center?
And two strong answers
out of the offerings come out on top. Public clouds such as Microsoft
Azure and Google Cloud, and a hybrid or multi-cloud approach. So again,
they're looking at the public clouds as a way to get off of their
traditional -- but they're looking not for just one or a lock-in, but
they're looking at a hybrid or multi-cloud approach.
Coming up zero, surprisingly,
is VMware on AWS, which you just mentioned, David. Private cloud
hosted and private cloud on-premises both come up at about 25 percent, along
with no plans to move. So, staying on-premises in a private cloud has traction
for some, but for those that want to move to the dominant hyperscalers,
a multi-cloud approach is clearly the favorite.
Linthicum: I thought there would be a few that would pick VMware on AWS, but it looks like the audience doesn't necessarily see that that's going to be the solution. Everything else is not surprising. It's aligned with what we see in the marketplace right now. Public cloud movement to Azure, Google Cloud and then also the movement to complex clouds like hybrid and multi-cloud also seem to be the two trends worth seeing right now in the space, and this is reflective of that.
Gardner: Let's move our discussion on. It's time to define the right trade-offs and rationale when we think about these taxing choices. We know that people want to improve, they don't want to be locked in, they want good economics, and they're probably looking for a long-term solution.
Now that we've
mentioned it several times, what is it about Azure and Azure Stack that
provides appeal? Microsoft’s cloud model seems to be differentiated in
the market, by offering both a public cloud component as well as an
integrated – or adjacent -- private cloud component. There’s a path for
people to come onto those from a variety of different deployment histories
including, of course, a Microsoft environment -- but also a VMware
environment. What should organizations be thinking about, what are the proper
trade-offs, and what are the major concerns when it comes to picking the
right hybrid and multi-cloud approach?
Strategic steps on the journey
Grimes: At the end of the day, it's ultimately a journey and that
journey requires a lot of strategy upfront. It requires a lot of planning,
and it requires selecting the right partner to help you through that
journey.
Because whether
you're planning an all-in on Azure, or an all-in on Google Cloud, or you
want to stay on VMware but get out of the enterprise data center, as
Dave has mentioned, the reality is everything is much more complex than it
seems. And to maximize the value of the models and capabilities that are
available today, you're almost necessarily going to end up in a hybrid
deployment model -- and that means you're going to have a mix of
technologies in play, a mix of skillsets required to support them.
Whether
you're planning on an all-Azure or all-Google, or you want to stay on
VMware, it's about getting out of the enterprise datacenter, and the
reality is far more complex than it seems.
Gardner: Dave, when you're looking at risk versus reward, cost versus benefits, when you're wanting to hedge bets, what is it about Microsoft Azure and Azure Stack in particular that help solve that? It seems to me that they've gone to great pains to anticipate the state of the market right now and to try to differentiate themselves. Is there something about the Microsoft approach that is, in fact, differentiated among the hyperscalers?
A seamless secret
Linthicum: The paired private and public cloud, with
similar infrastructures and similar migration paths, and dynamic migration
paths, meaning it could be workloads in between them -- at least this is
the way that it's been described -- is going to be unique in the market. Kind
of the dirty little secret.
It's going to be
very difficult to port from a private cloud to a public cloud because
most private clouds are typically not AWS and not Google, and they don't
make private clouds. Therefore, you have to port your code between the two,
just like you've had to port systems in the past. And the normal issues
about refactoring and retesting, and all the other things, really come home to
roost.
But Microsoft
could have a product that provides a bit more of a seamless capability
of doing that. And the great thing about that is I can really localize on
whatever particular platform I'm looking at. And if I, for example, “mis-localize”
or I misfit, then it's a relatively easy thing to move it from private to
public or public to private. And this may be at a time where the market
needs something like that, and I think that's what is unique about it in
the space.
Gardner: Tim, what do you see as some of the trade-offs, and what is it about a public, private hybrid cloud that's architected to be just that -- that seemingly Microsoft has developed? Is that differentiating, or should people be thinking about this in a different way?
Crawford: I actually think it's significantly differentiating, especially when you consider the complexity that exists within the mass of the enterprise. You have different needs, and not all of those needs can be serviced by public cloud, not all of those needs can be serviced by private cloud.
Gardner: Tim, what do you see as some of the trade-offs, and what is it about a public, private hybrid cloud that's architected to be just that -- that seemingly Microsoft has developed? Is that differentiating, or should people be thinking about this in a different way?
Crawford: I actually think it's significantly differentiating, especially when you consider the complexity that exists within the mass of the enterprise. You have different needs, and not all of those needs can be serviced by public cloud, not all of those needs can be serviced by private cloud.
There's a model
that I use with clients to go through this, and it's something that I
used when I led IT organizations. When you start to pick apart these
pieces, you start to realize that some of your components are well-suited
for software as a service (SaaS)-based alternatives, some of the
components and applications and workloads are well-suited for public
cloud, some are well-suited for private cloud.
A good example of that is if you have sovereignty issues, or compliance and regulatory issues. And then you'll have some applications that just aren't ready for cloud. You've mentioned lift and shift a number of times, and for those that have been down that path of lift and shift, they've also gotten burnt by that, too, in a number of ways.
A good example of that is if you have sovereignty issues, or compliance and regulatory issues. And then you'll have some applications that just aren't ready for cloud. You've mentioned lift and shift a number of times, and for those that have been down that path of lift and shift, they've also gotten burnt by that, too, in a number of ways.
And so, you have to be mindful of what applications go in
what mode, and I think the fact that you have a product like Azure Stack
and Azure being similar, that actually plays pretty well for an enterprise
that's thinking about skillsets, thinking about your development cycles,
thinking about architectures and not having to create, as Dave
was mentioning, one for private cloud and a completely different
one for public cloud. And if you get to a point where you want to move
an application or workload, then you're having to completely redo it over
again. So, I think that Microsoft combination is pretty unique, and will
be really interesting for the average enterprise.
Gardner: From the managed service provider (MSP) perspective, at Navisite you have a large and established hosted VMware business, and you’re helping people transition and migrate. But you're also looking at the potential market opportunity for an Azure Stack and a hosted Azure Stack business. What is it for the managed hosting provider that might make Microsoft's approach differentiated?
Gardner: From the managed service provider (MSP) perspective, at Navisite you have a large and established hosted VMware business, and you’re helping people transition and migrate. But you're also looking at the potential market opportunity for an Azure Stack and a hosted Azure Stack business. What is it for the managed hosting provider that might make Microsoft's approach differentiated?
A full-spectrum solution
Grimes: It comes down to what both Dave and Tim mentioned. Having a
light stack and being able to be deployed in a private capacity,
which also -- by the way -- affords the ability to use bare metal
adjacency, is appealing. We haven't talked a lot about bare metal, but it is something
that we see in practice quite often. There are bare metal workloads that need
to be very adjacent, i.e. land adjacent, to the virtualization-friendly
workloads.
Being able
to have the combination of all three of those things is what makes AzureStack attractive to a hosting provider such as Navisite. With it, we can
solve the full-spectrum of the needs of the client, covering bare metal,
private cloud, and hyperscale public -- and really in a seamless way --
which is the key point.
Gardner: It's not often you can be as many things to as many people as that given the heterogeneity of things over the past and the difficult choices of the present.
Gardner: It's not often you can be as many things to as many people as that given the heterogeneity of things over the past and the difficult choices of the present.
We have been
talking about these many cloud choices in the abstract. Let's now go to a
concrete example. There's an organization called Ceridian. Tell us about how they solved their requirements problems?
Azure
Stack is attractive to a hosting provider like Navisite. With it we can
solve the full-spectrum of the needs of the client in a seamless way.
But one thing
about Ceridian is they have had a cloud-first strategy. They embraced
the cloud very early. A lot of those barriers to entry that we saw,
and have seen over the years, they looked at as opportunity, which
I find very interesting.
Requirements around security and compliance are critical
to them, but they also recognized that a SaaS provider that does a very
small set of IT services -- delivering managed infrastructure with
security and compliance -- is actually likely to be able to do that at
least as effectively, if not more effectively, than doing it in-house, and
at a competitive and compelling price point as well.
So some of their challenges really were around all the reasons that we see, that we talked about here today, and see as the drivers to adopting cloud. It's about enabling business agility. With the growth that they've experienced, they've needed to be able to react quickly and deploy quickly, and to leverage all the things that virtualization and now cloud enable for the enterprises. But again, as I mentioned before, they worked closely with a partner to maximize the value of the technologies and ensure that we're meeting their security and compliance needs and delivering everything from a managed infrastructure perspective.
So some of their challenges really were around all the reasons that we see, that we talked about here today, and see as the drivers to adopting cloud. It's about enabling business agility. With the growth that they've experienced, they've needed to be able to react quickly and deploy quickly, and to leverage all the things that virtualization and now cloud enable for the enterprises. But again, as I mentioned before, they worked closely with a partner to maximize the value of the technologies and ensure that we're meeting their security and compliance needs and delivering everything from a managed infrastructure perspective.
Overcoming geographical barriers
One of the core challenges that they had with that growth was
a need to expand into geographies where we don't currently operate
our hosting facilities, so Navisite's hosting capabilities. In
particular, they needed to expand into Australia. And so, what we were
able to do through our partnership with Microsoft was basically deliver to
them the managed infrastructure in a similar way.
This is actually
an interesting use case in that they're running VMware-based cloud in our
data center, but we were able to expand them into a managed Azure-delivered
cloud locally out of Australia. Of course, one thing we didn't touch on
today -- but is a driver in many of these decisions for global
organizations -- is a lot of the data sovereignty and locality regulations are
becoming increasingly important. Certainly, Microsoft is expanding the
Azure platform. And so their presence in Australia has enabled us to
deliver that for Ceridian.
As I think about the key takeaways and learnings from this particular example, Ceridian had a very clear, very well thought out cloud-centric and cloud-first strategy. You, Dana, mentioned it earlier, that that really enables them to continue to keep their focus on the applications because that's their bread and butter, that's how they differentiate.
As I think about the key takeaways and learnings from this particular example, Ceridian had a very clear, very well thought out cloud-centric and cloud-first strategy. You, Dana, mentioned it earlier, that that really enables them to continue to keep their focus on the applications because that's their bread and butter, that's how they differentiate.
By partnering, they're able to not worry about the keeping
the lights on and instead focus on the application. Second, of course, is
they're a global organization and so they have global delivery needs based
on data sovereignty regulations. And third, and I'd say probably most
important, is they selected a partner that was able to bring to bear the
expertise and skillsets that are difficult for enterprises to recruit and
retain. As a result, they were able to take advantage of the different
infrastructure models that we're delivering for them to support their
business.
Gardner: We're now going to go to our question and answer portion. Kristen Allen of Navisite is moderating our Q and A section.
Gardner: We're now going to go to our question and answer portion. Kristen Allen of Navisite is moderating our Q and A section.
Bare metal and beyond
Kristen Allen: We have some very interesting questions. The first one ties into
a conversation you were just having, "What are the ROI benefits to moving
to bare metal servers for certain workloads?"
Grimes: Not all software licensing is yet virtualization-friendly, or at least on a virtualization platform-agnostic platform, and so there's really two things that play into the selection of bare metal, at least in my experience. There is kind of a model of bare metal computing, small cartridge-based computers, that are very specific to certain workloads. But when we talk in more general terms for a typical enterprise workload, it really revolves around either software licensing incompatibility with some of the cloud deployment models or a belief that there is a performance that requires bare metal, though in practice I think that's more of optics than reality. But those are the two things that typically drive bare metal adoption in my experience.
Linthicum: Ultimately, people want access directly for at the end-of-the-line platforms, and if there's some performance reason, or some security reason, or some kind of a direct access to some of the input-output systems, we do see these kinds of one-offs for bare metal. I call them special needs applications. I don't see it as something that's going to be widely adopted, but from time to time, it's needed, and the capabilities are there depending on where you want to run it.
Allen: Our next question is, "Should there be different thinking for data workloads versus apps ones, and how should they be best integrated in a hybrid environment?"
Grimes: Not all software licensing is yet virtualization-friendly, or at least on a virtualization platform-agnostic platform, and so there's really two things that play into the selection of bare metal, at least in my experience. There is kind of a model of bare metal computing, small cartridge-based computers, that are very specific to certain workloads. But when we talk in more general terms for a typical enterprise workload, it really revolves around either software licensing incompatibility with some of the cloud deployment models or a belief that there is a performance that requires bare metal, though in practice I think that's more of optics than reality. But those are the two things that typically drive bare metal adoption in my experience.
Linthicum: Ultimately, people want access directly for at the end-of-the-line platforms, and if there's some performance reason, or some security reason, or some kind of a direct access to some of the input-output systems, we do see these kinds of one-offs for bare metal. I call them special needs applications. I don't see it as something that's going to be widely adopted, but from time to time, it's needed, and the capabilities are there depending on where you want to run it.
Allen: Our next question is, "Should there be different thinking for data workloads versus apps ones, and how should they be best integrated in a hybrid environment?"
The
compute aspect and data aspect of an application should be decoupled.
If you want to you can then assemble them on different platforms, even
one on public cloud and one on private cloud.
As we're migrating
forward, the workloads are getting even more complex. And there's some
application workloads that I've seen, that I've developed, where the
database would be partitioned against the private cloud and the public
cloud for disaster recovery (DR) purposes or performance purposes, and things
like that. So, it's really up to you as the architect as
to where you're going to place the data in adjacent relation to the
workload. Typically, a good idea to place them as close to each other as
they can so they have the highest bandwidth to communicate to each other.
However, it's not necessary depending on what the application's doing.
Gardner: David, maybe organizations need to place their data in a certain jurisdiction but might want to run their apps out of a data center somewhere else for performance and economics?
Grimes: The data sovereignty requirement is something that we touched on and that's becoming increasingly important and increasingly, that's a driver too, in deciding where to place the data.
Gardner: David, maybe organizations need to place their data in a certain jurisdiction but might want to run their apps out of a data center somewhere else for performance and economics?
Grimes: The data sovereignty requirement is something that we touched on and that's becoming increasingly important and increasingly, that's a driver too, in deciding where to place the data.
Just following on
Dave's comments, I agree 100 percent. If you have the opportunity to
architect a new application, I think there's some really interesting
choices that can be made around data placement, network placement,
and decoupling them is absolutely the right strategy.
I think the challenge
many organizations face is having that mandate to close down the
enterprise data center and move to the "cloud." Of course, we
know that “cloud” means a lot of different things but, do that in a legacy application
environment and that will present some unique challenges as well, in terms
of actually being able to sufficiently decouple data and applications.
Curious, Dave,
if you've had any successes in kind of meeting that challenge?
Linthicum: Yes. It depends on the application workload and how flexible the applications are and how the information is communicating between the systems; also security requirements. So, it's one of those obnoxious consulting responses, “it depends” as to whether or not we can make that work. But the thing is the architecture is a legitimate architectural pattern that I've seen before and we've used it.
Allen: Okay. How do you meet and adapt for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) requirements and still maintain stable connectivity for the small business?
Grimes: HIPAA, like many of the governance programs, is a very large and co-owned responsibility. I think from our perspective at Navisite, part of Spectrum Enterprise, we have the unique capability of delivering both the network services and the cloud services in an integrated way that can address the particular question around stable connectivity. But ultimately, HIPAA is a blended responsibility model where the infrastructure provider, the network provider, the provider managing up to whatever layer of the application stack will have certain obligations. But then the partner, the client would also retain some obligations as well.
Linthicum: Yes. It depends on the application workload and how flexible the applications are and how the information is communicating between the systems; also security requirements. So, it's one of those obnoxious consulting responses, “it depends” as to whether or not we can make that work. But the thing is the architecture is a legitimate architectural pattern that I've seen before and we've used it.
Allen: Okay. How do you meet and adapt for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) requirements and still maintain stable connectivity for the small business?
Grimes: HIPAA, like many of the governance programs, is a very large and co-owned responsibility. I think from our perspective at Navisite, part of Spectrum Enterprise, we have the unique capability of delivering both the network services and the cloud services in an integrated way that can address the particular question around stable connectivity. But ultimately, HIPAA is a blended responsibility model where the infrastructure provider, the network provider, the provider managing up to whatever layer of the application stack will have certain obligations. But then the partner, the client would also retain some obligations as well.
Listen to the podcast. Find it on iTunes. Read a full transcript or download a copy. Sponsor: Sponsor: Navisite.
You may also be
interested in:
- Containers, microservices, and HCI help governments in Norway provide safer public data sharing
- Balancing costs with conscience--How new tools help any business build ethical and sustainable supply chains
- Panel explores new ways to solve the complexity of hybrid cloud monitoring
- Pay-as-you-go IT models provide cost and operations advantages for Northrop Grumman
- Ericsson and HPE accelerate digital transformation via customizable mobile business infrastructure stacks
- A tale of two hospitals—How healthcare economics in Belgium hastens need for new IT buying schemes
- How VMware, HPE, and Telefonica together bring managed cloud services to a global audience
- Inside story on HPC's role in the Bridges Research Project at Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center
- As enterprises face mounting hybrid IT complexity, new management solutions beckon